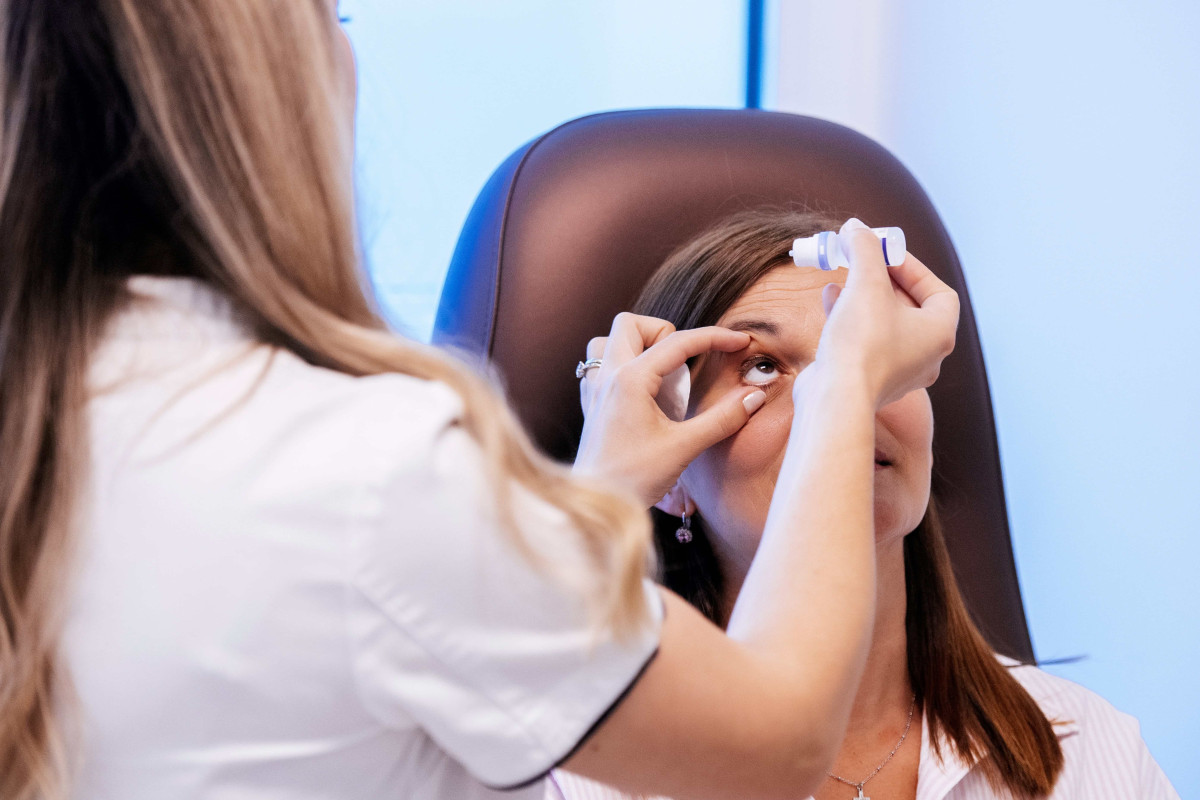
Dry eye syndrome has become a common issue in the modern era, especially among people who spend a lot of time in front of computer screens or air-conditioned environments. This syndrome can significantly impact quality of life, causing discomfort, irritation, and vision problems. Recognizing symptoms and timely treatment are crucial for maintaining eye health and preventing long-term complications. In this article, we will explore what dry eye syndrome is, its symptoms, treatment methods, and provide tips for prevention and symptom relief.
Dry eye syndrome is a condition that occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when tears are of poor quality, leading to dryness and irritation of the eye surface. Tears are crucial for maintaining eye health as they provide necessary moisture, lubrication, nutrients, and protection against infections. When tears lack these essential elements, it can lead to damage to the eye surface and inflammatory processes.
Several factors can contribute to the development of dry eye syndrome:
- Aging: With age, natural tear production may decrease.
- Environmental factors: Climate, wind, smoke, and dry air can accelerate tear evaporation.
- Prolonged screen use: Staring at a screen reduces blinking frequency, which decreases tear distribution over the eye surface.
- Contact lens wear: Contact lenses can absorb tears and cause dryness.
- Medical conditions: Certain diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid problems can affect tear production.
- Medications: Some medications, like antihistamines, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, can reduce tear production.
Understanding the causes of dry eye syndrome is crucial for its effective treatment. If you notice symptoms such as burning sensation, itching, redness, blurred vision, or a sensation of grittiness in the eyes, it's important to consult an ophthalmologist. Timely diagnosis can prevent further complications and help maintain optimal eye health.
Dry eye syndrome can be managed with a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes. Below, we'll detail the symptoms of this syndrome, available treatment methods, and tips for prevention and symptom relief.
How to Recognize and Treat Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome has become a common issue in the modern era, especially among people who spend a lot of time in front of computer screens or in air-conditioned environments. This syndrome can significantly impact quality of life, causing discomfort, irritation, and vision problems. Recognizing symptoms and timely treatment are key to maintaining eye health and preventing long-term complications. In this article, we'll explore what dry eye syndrome is, its symptoms, treatment options, and provide tips for prevention and symptom relief.
Symptoms of Dry Eye Syndrome
Recognizing symptoms of dry eye syndrome can be crucial for timely treatment. The most common symptoms include:
- Feeling of dryness: Feeling dryness or lack of moisture in the eyes.
- Burning sensation: Feeling burning or itching in the eyes.
- Blurry vision: Occasional blurry vision, especially after prolonged screen viewing.
- Redness: Eye redness caused by irritation.
- Light sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light or photophobia.
- Feeling of grittiness: Sensation of a foreign body or grittiness in the eyes.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is recommended to visit an ophthalmologist for diagnosis and advice on appropriate treatment. Symptoms may worsen throughout the day, especially after activities that require intense focus, such as reading or computer work.
Treatment Methods for Dry Eye Syndrome
Treatment of dry eye syndrome depends on the cause and severity of symptoms. Common treatment methods include:
- Artificial tears: Using artificial tears or lubricating eye drops to provide additional moisture.
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyes to stimulate natural tear production.
- Hydrating gels: Using hydrating gels or ointments, especially at night, to maintain eye moisture.
- Environmental changes: Introducing humidifiers into rooms or avoiding dry and air-conditioned air.
- Medications: In some cases, the doctor may recommend medications that stimulate tear production or reduce inflammation.
- Surgical procedures: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as closing tear ducts may be considered to reduce tear evaporation.
It is important to consult with an ophthalmologist before starting any treatment to select the most appropriate method for your specific case. Regular eye exams can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
Tips for Prevention and Symptom Relief
In addition to treatment, there are measures you can take to prevent dry eye syndrome or alleviate symptoms:
- Blink regularly: Make sure to blink regularly, especially when working at a computer, to evenly distribute tears over the eye surface.
- Take breaks during work: Take frequent breaks during prolonged computer work or reading to reduce eye strain.
- Use humidifiers: Use humidifiers in rooms with dry air to maintain optimal humidity.
- Eye protection: Wear sunglasses that block wind and UV rays to protect the eyes from irritation.
- Avoid irritants: Avoid smoke, dust, and other irritants that can worsen dry eye symptoms.
- Healthy diet: Consume enough omega-3 fatty acids that can help maintain eye health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Adhering to these tips can significantly reduce the risk of developing dry eye syndrome and help maintain eye health.
If symptoms persist despite these measures, it is important to revisit an ophthalmologist for further evaluation and adjustment of treatment. An ophthalmologist will be able to provide additional recommendations or change therapy to achieve better management of dry eye syndrome.
Some people may require a combination of different therapeutic approaches to achieve optimal results. In some cases, especially when the cause of dry eye syndrome is a medical condition or taking certain medications, long-term symptom management and regular check-ups may be necessary to adjust treatment according to changes in health status.
Continuing to practice preventive measures is important to reduce the risk of worsening the condition. Regular eye exams, adherence to lifestyle advice, and timely response to changes in symptoms are crucial for maintaining eye health and quality of life.
Dry eye syndrome can be persistent, but with proper management and collaboration with a medical professional, most people can achieve significant improvement in symptoms and preserve eye health in the long term.